Creating Cloudentity policies in the Visual Policy Editor
Instructions on how to create a policy to verify requests based on your access control requirements using the Cloudentity policy editor.
Create Policy
Check the video and the procedure below to learn how to create a policy in Cloudentity. Policies are created per workspace and the workspace name is automatically added as a prefix to the policy ID.
Select Authorization > Policies > + CREATE POLICY.
Fill in the policy form. Make sure to select the correct policy type as explained in the table above.
Select Create.
The policy editor opens.
Define the policy using dedicated validators. Note that you can only add validators relevant to the selected policy type. Check the validator list below for more information.
Wildcards Pattern Matching
Warning
This feature works in the Cloudentity policy editor only - it's not available for Rego policies.
When creating policies, you can match values to a pattern using the * character. Consider the policy comparator below:
{
"fields":[
{
"field":"sub",
"comparator":"equals",
"value":"admin-*"
}
]
}Such comparator matches all values with the admin- prefix, such as admin-123.
In the editor UI, the above implementation would look as follows:
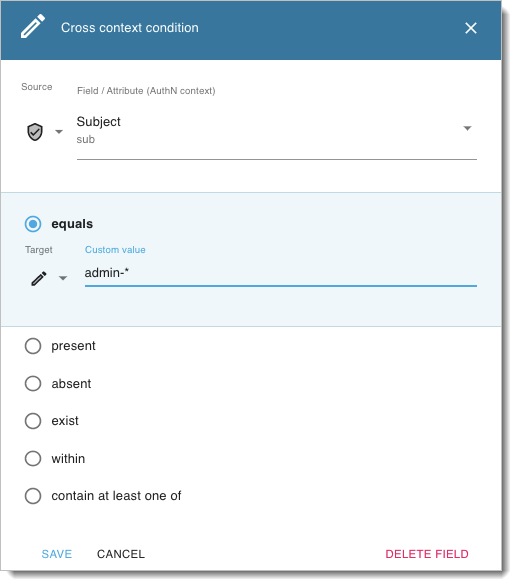 |
If you want the * character to be interpreted literally, escape it with \ as shown below:
{
"fields":[
{
"field":"group",
"comparator":"equals",
"value":"\*"
}
]
}Such comparator matches * only.
Attributes Validator
Attribute validator is a generic validator allowing you to compare any source valid for the selected policy type
Authentication context attribute
Access token claims
ID token claims
Secrets
Scopes
against any target valid for the selected policy type. Note that it might be easier to add and set up dedicated validators, where you have fewer source/target options.
In the video below, we are creating a policy checking if the request comes from a client application registered within a specific tenant.
Authentication Context Validator
Authentication context validator allows you to check an authentication context attribute against
a specific value
another authentication context attribute
In the video below, we are creating a policy checking that the IDP used to authenticate is registered in Cloudentity under the name github.
Client Validator
Client validator can validate the client context attributes in the request, passed in the contexts.client object. This way, you can verify any client registered in Cloudentity. For a list of client parameters, see the Client API documentation.
In the video below, we are creating a policy checking a specific client attribute (attribute_name). We expect this attribute to have a specific value.
This policy passes when the following client data is present in the request:
"contexts": {
"client": {"attribute_name": "value"}
}Developer Validator
Developer validator can validate the developer context attributes in the request, passed in the contexts.developer object.
In the video below, we are creating a policy checking a specific developer attribute (attribute_name). We expect this attribute to have a specific value.
This policy passes when the following developer data is present in the request:
"contexts": {
"developer": {"attribute_name": "value"}
}Embedded Policy Validator
Embedded policy validator allows you to pick another policy of the same type and resolve it within this validator. This way, you can nest policies within other policies.
Embedded REGO policies for Istio header injection
To learn more, see Header injection for Istio policies.
Authentication Factors (MFA) Validator
Authentication factors validator checks if the user has completed the MFA process and prompts the user to do so if they didn't.
ID Token Validator
ID token validator compares an ID token attribute to a specific value or another ID token attribute.
Request Header Validator
Request header validator allows you to check a specific header for value or presence. In the video below, we are creating a policy checking for a specific header value.
Logical Validators
By default, the policy checks all of its validators and passes only if all of them are resolved as true. It is however possible to create a conditional policy which allows you to build if/else statements based on validators, as shown in the video example below.
The Fail and Pass validators end policy resolution.
Signal Validator
The Signal validator is useful when your requests are protected via Signal Sciences, allowing you to check the Signal warnings in order to validate the policy. You can check for the presence or absence of warnings.
Software Statement Validator
When client registration in Cloudentity is protected by a software statement assertion (SSA), you can use this validator to further restrict client registration based on certain parameters in the SSA, as shown in the video below.
This policy passes when the following client data is present in the request:
"contexts": {
"softwareStatement": {"attribute_name": "value"}
}Test Your Policy
You can test your policy in Test mode against a sample input which is intended to mimic a real request. Edit the input so that it matches the request you expect this policy to receive and run the policy to see if you get the expected outcome.
In the video below, we are verifying the name attribute from the authentication context against a specific value.