Integrate third-party applications for authentication
Enhance your authentication processes by integrating third-party applications with SecureAuth. This integration allows you to enrich the user's authentication context, ensuring a comprehensive and secure user experience. By connecting external applications, you can prompt users for additional information post-authentication, tailoring the authentication flow to your organization's specific requirements.
Register an application
-
Go to Extensions > Extension Apps.
-
Click Custom Application.
-
Enter the application details:
Field Value Type Set the application type. Name Name to identify the application. Application URL Provide the third-party application URL where SecureAuth will redirect users during authentication. -
Click Create.
Result: SecureAuth adds your application as a client in the system workspace. It generates a Client ID and Client Secret, allowing your application to authenticate with SecureAuth and perform operations.
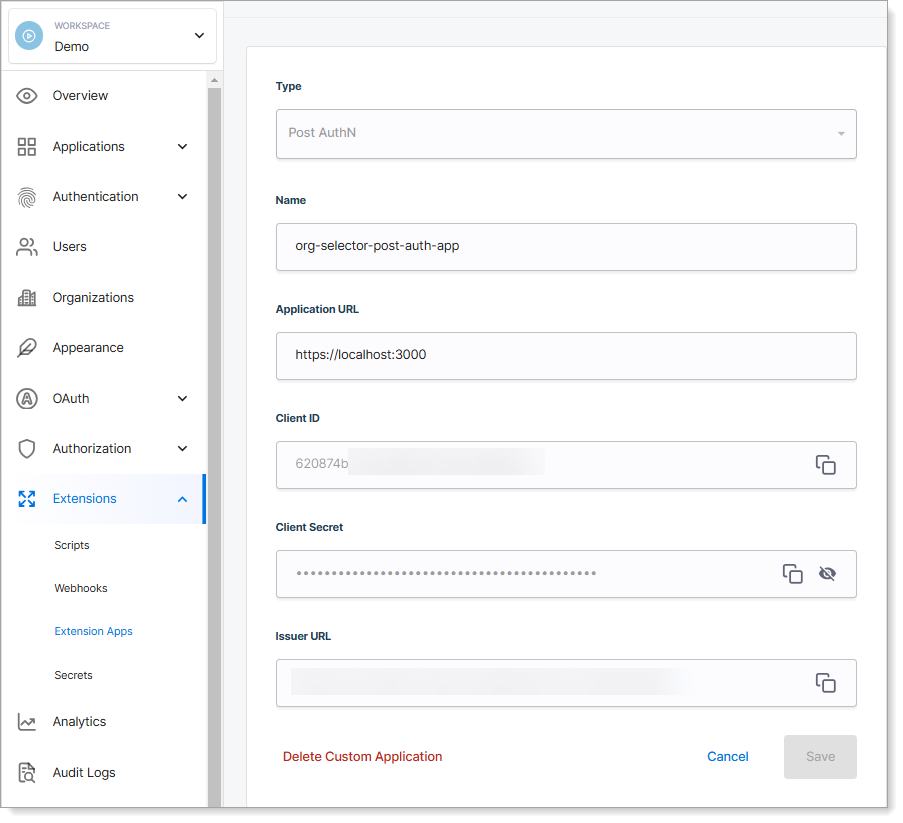
Third-party application registration example
Associate an application with an IDP
-
Go to Authentication > Providers, and select an IDP.
-
Select the Extensions tab.
-
In the Post Authentication application field, select your application.
Result: Users are redirected to the selected application after login.
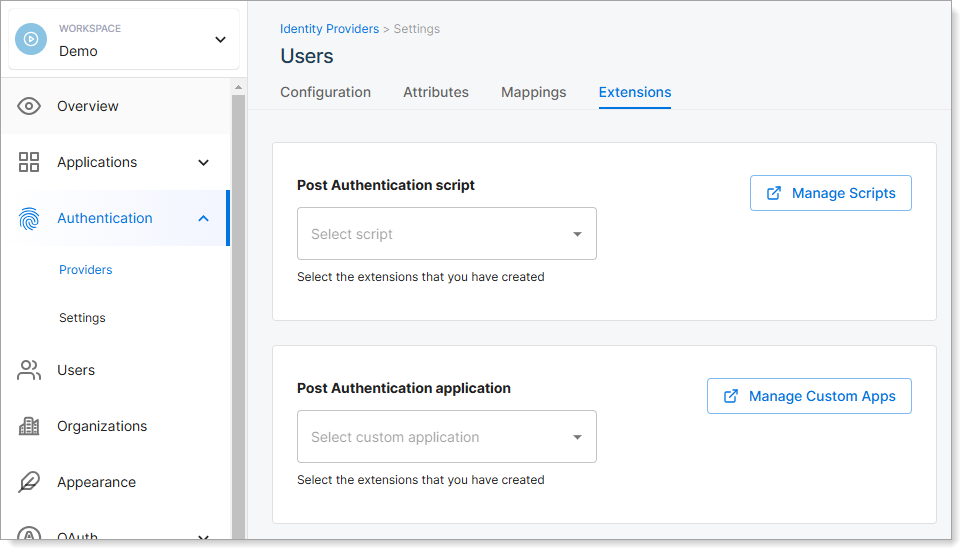
Third-party application association example
Post-authentication success flow
Use case: After authentication, a third-party application collects additional user information and updates the user's authentication context.
Abstract flow
Post-authentication success flow
-
User authentication. SecureAuth authenticates the user.
-
Redirect to application. SecureAuth redirects to the
Application URLspecified in the custom application configuration, includinglogin_idandlogin_statequery parameters.For example:
https://myapplication.com?login_id=REDACTED&login_state=REDACTED -
Third-party authentication. The application authenticates with SecureAuth using the
client_secret_basicmethod and client credentials.To learn more, see POST Authn-client-secret-basic
-
Retrieve user session. Fetch the user's session using GET post-authn-session.
-
Collect additional information. Retrieve data from a third-party data store and display options to the user.
-
Update authentication context:
-
User selects an option and submits.
-
Include the selected values in the authentication context.
JSON example:
{
"authentication_context":{ # User's authentication context
"organizationId":"6502", # Additional attributes
"organizationName":"Acme Inc.",
"permissions":[
"acme:ViewDashboard",
"acme:CreateOrder",
"acme:ViewOrder"
]
},
"id":"REDACTED", # Required login_id
"login_state":"REDACTED" # Required login_state
}
-
-
Complete post-authentication flow. Send the context to SecureAuth via POST post-authn-complete.
-
Redirect. SecureAuth responds with a redirect URL for the next step in the authentication process.
For example:
{
"redirect_to":"https://my-tenant.us.connect.secureauth.com/my-tenant/my-workspace/oauth2/authorize?..."
} -
Continue authentication. Redirect the user to the
redirect_toURL. -
SecureAuth proceeds to the next step in the authentication process.
Post-authentication abort flow
Use case: The third-party application fails to complete the process due to an error or missing user data.
-
User authentication. SecureAuth authenticates the user.
-
Redirect to application. SecureAuth redirects to the
application URLwithlogin_idandlogin_state.For example:
https://myapplication.com?login_id=qwerty&login_state=asdfg -
Third-party authentication. The application authenticates with SecureAuth using client credentials.
-
Retrieve user session. Fetch the user's session using GET post-authn-session.
-
Error handling. If an error occurs or user data is insufficient:
-
Construct an abort JSON.
For example:
{
"status":403,
"error":"AccessDenied",
"error_description":"User denied access",
"id":"REDACTED",
"login_state":"REDACTED"
} -
Send the abort JSON to SecureAuth via POST post-authn-abort.
-
-
Redirect. SecureAuth responds with a redirect URL for an error page.
For example:
{
"redirect_to":"https://my-tenant.us.connect.secureauth.com/my-tenant/my-workspace/oauth2/authorize?..."
} -
Error display:
-
Redirect to SecureAuth to display a generic authentication failure message.
-
Alternatively, display the third-party error page without returning to SecureAuth.
-
