Blocking rules settings in a policy
Blocking rules are evaluated first before authentication rules. When the behavior of a user login triggers any one of the blocking rules, it provides a hard stop and prevents access to a resource.
With a policy open in edit mode, select the Blocking Rules tab.
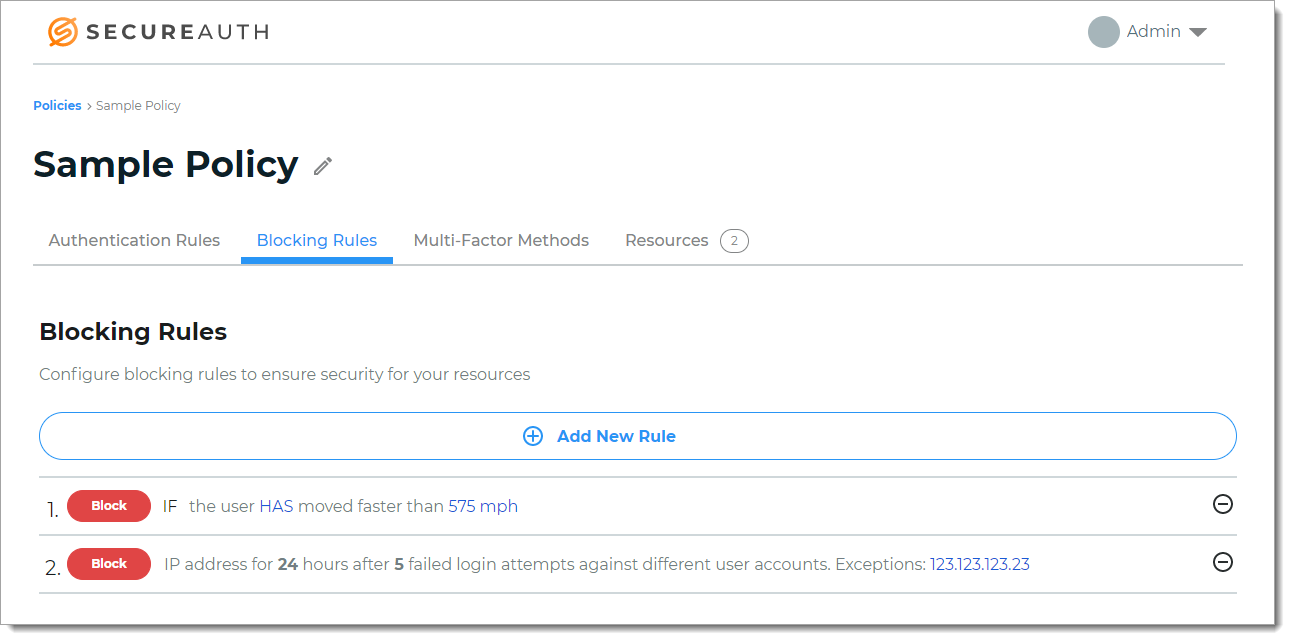
When modifying a rule, you can do any of the following:
To remove a rule, click the minus icon.
To change the properties of the rule, use the clickable rule links.
To add a new blocking rule, click Add New Rule and choose from the following rule types:
Dynamic IP Blocking
Rule to block access for a length of time after a set number of failed login attempts against different usernames.
For example, if there are password spraying and other online password attacks using different usernames, it blocks login attempts coming from that IP address. After 15 failed login attempts, it blocks the IP address for 24 hours.
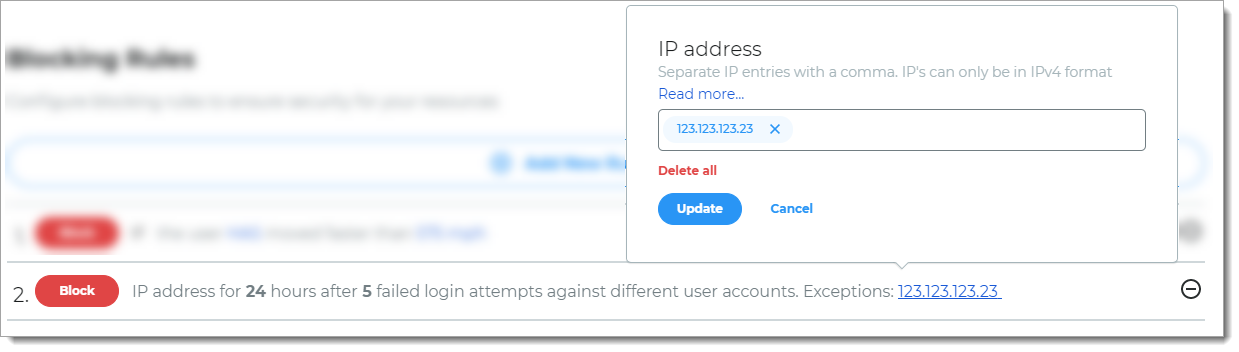
The IP Filtering rule determines the IP blocking values and the allowed global IP addresses. You can add more allowed IP addresses for a specific policy by clicking the Allowed IP Addresses links.
For example, you might have a policy specific to contractors and you can add allowed IP addresses to check in addition to the defined IP Filtering rule.
Applies to Identity Platform version 20.06 or later.
Dynamic Perimeter
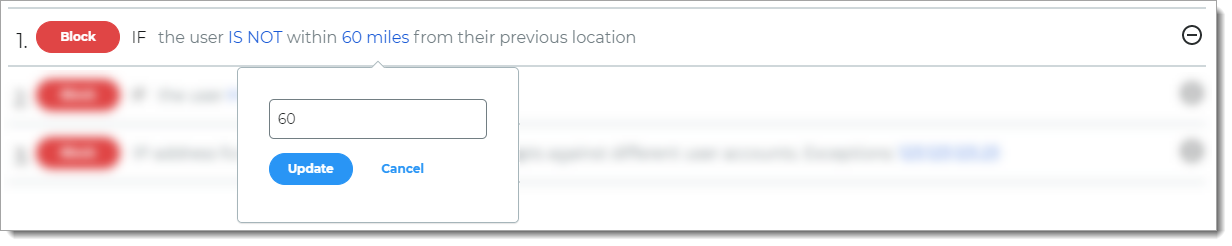
Rule to determine access based on whether the user login is or is not within a set distance from the previous location.
For example, if the user login is more than 60 miles from the previous location, it blocks the login attempt.
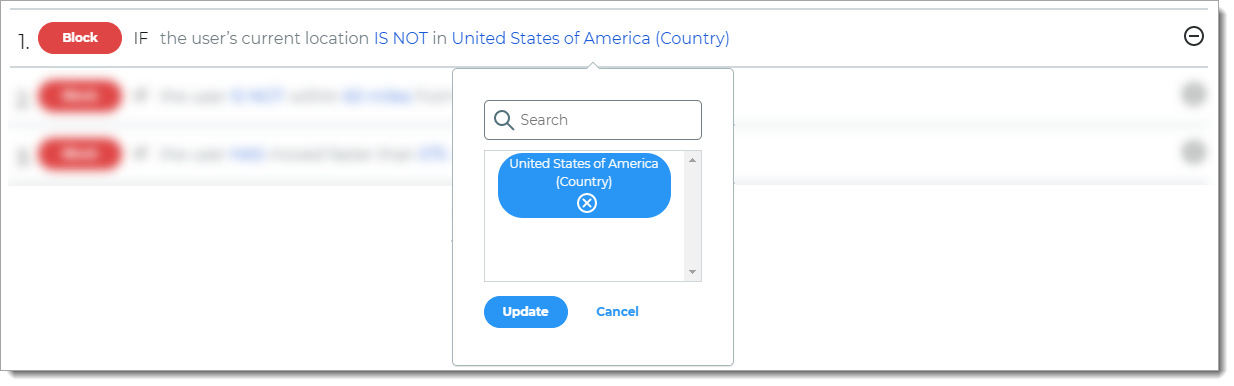
Country
Rule to determine access based on whether the user login is or is not within a defined country.
For example, if the user login is NOT in the United States, then it blocks the login attempt.
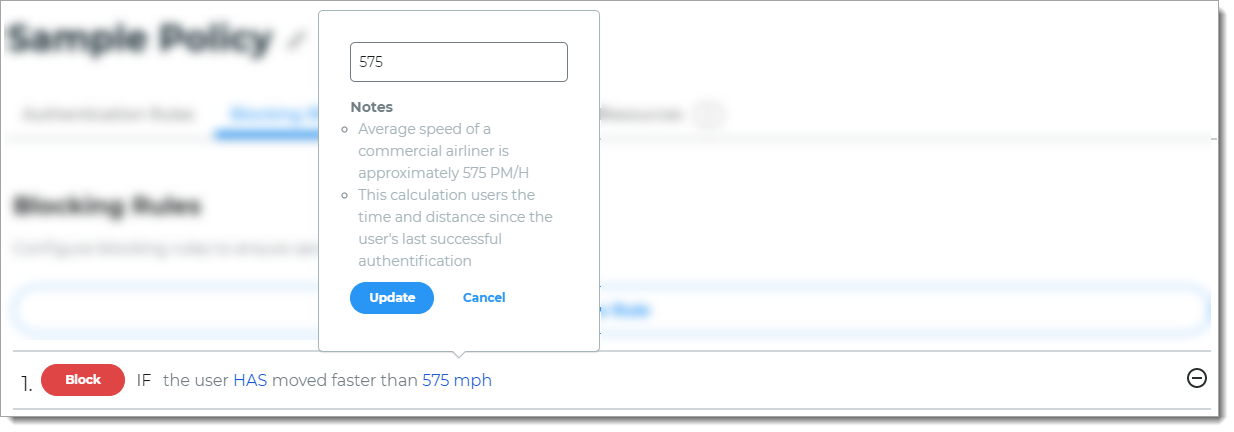
Geo-velocity
Rule to determine access based on the speed of travel between the previous login and current login attempt.
For example, if the user logged in from Los Angeles, California (point A) at 11:15 a.m. and then from New York, New York (point B) at 11:45 a.m. on the same day, then it blocks the login attempt.
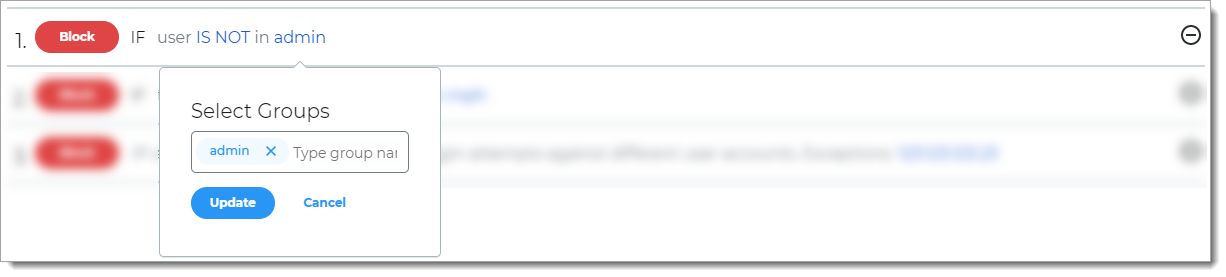
Group
Rule to determine access based on group membership.
For example, if the user is not a member of a specified group, then it blocks the login attempt.
Note
Before you can use this rule, you must define the groups in the data store for your organization.
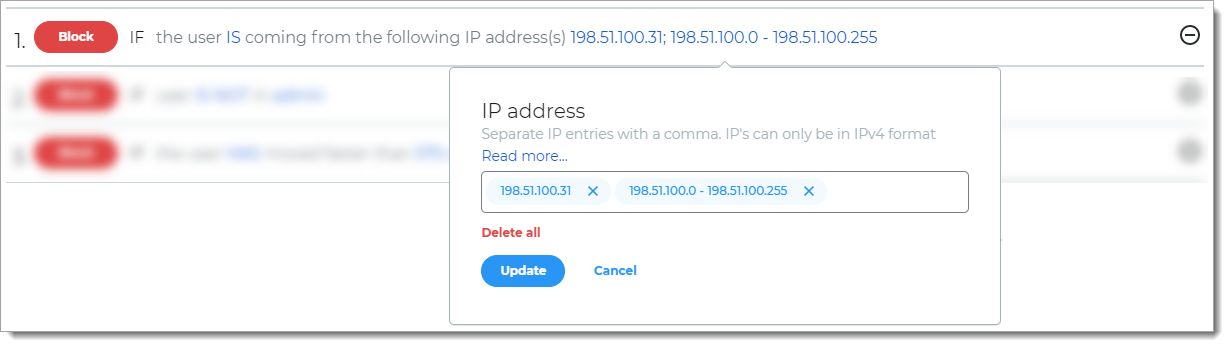
IP Range
Rule to block access based on IP ranges. You can enter individual values or a range of values in IPv4 format.
For example, if the user login comes from any of the specified IP addresses, then it blocks the login attempt.
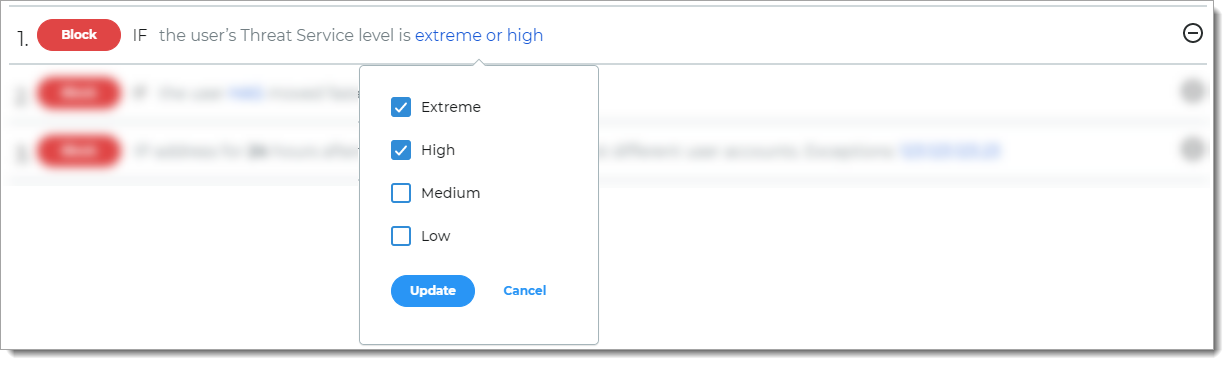
Threat Service
Rule to determine access based on known risks associated with the login attempt as determined by the SecureAuth Threat Service.
For example, if the user login is associated with a known threat, then it blocks the login attempt.
Note
You must have a license to use this feature. To learn more about the Threat Service rule, contact your SecureAuth Account Manager.
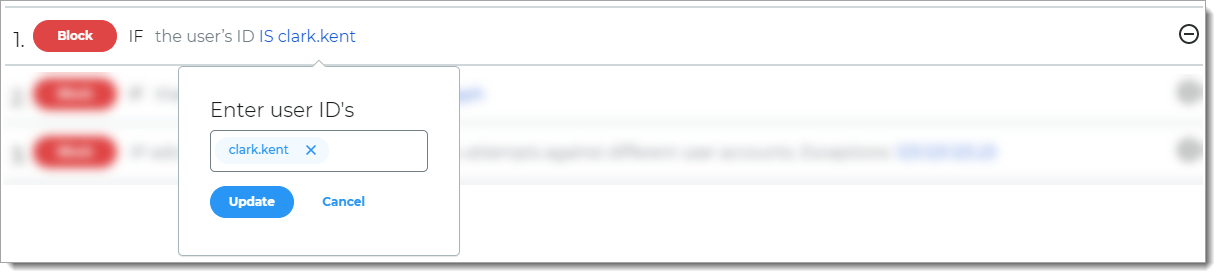
User
Rule to determine access based on whether the user login is the same as the specified user ID.
For example, if the user login matches the user ID, then it blocks the login attempt.
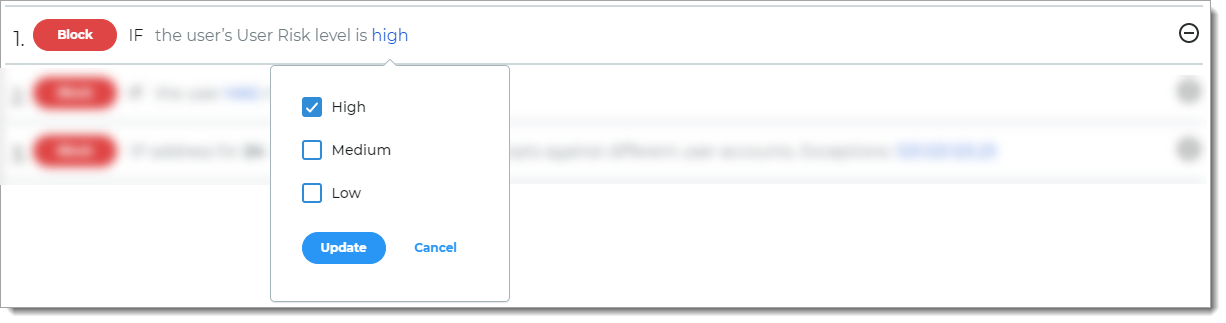
User Risk
Rule to determine access based on user reputation and behavior factors associated with the login attempt.
For example, if the login reputation and behavior of the user falls into the specified risk level, then it blocks the login attempt.
Note
You must have a license to use this feature. To learn more about the User Risk rule, contact your SecureAuth Account Manager.
Save your changes.