Troubleshooting Login for Windows
This topic contains information about logs and troubleshooting Login for Windows.
SecureAuth Identity Platform transaction log information
The Login for Windows software issues a User-Agent HTTP request header when the API interacts with the Identity Platform. The following items are included in the User-Agent string:
Login for Windows software version
OS version
Computer name (hostname)
Time zone
IP address
MAC address
For example,
SecureAuth Login for Windows 21.04.00 (Windows 10 Pro x64 6.2.9200; LT-JSMITH; (UTC-05:00) Eastern Standard Time; 111.22.333.44; 0f:10;35:7a:81:4e)
Error logs
You can find Login for Windows error logs in the following locations.
Installation logs
Installation log information writes to the install.log file.
Windows 11 and later:
c:\Windows\SystemTemp\install.log
Windows Server 2022 and later:
c:\Windows\SystemTemp\install.log
Other Windows versions:
%temp%\install.log
Login logs
Login information writes to the login.log file:
C:\ProgramData\SecureAuth\login.log
The login.log log file displays system information, such as the type and version of the operating system, the version of Login for Windows your organization is running, and more as shown next:
*************************************************************** *** LocalComputerName: *** OSVersion: *** Uptime: *** LocalLanguageName: *** TimeZone: *** ProductName: ***************************************************************
After you view the login.log file, then connect later through RDP, you might see what look like inconsistencies because the log file will have new start lines and threads. This is expected behavior because connecting through RDP causes new instances of the credential provider to be created, which causes the new start lines and threads.
Troubleshooting
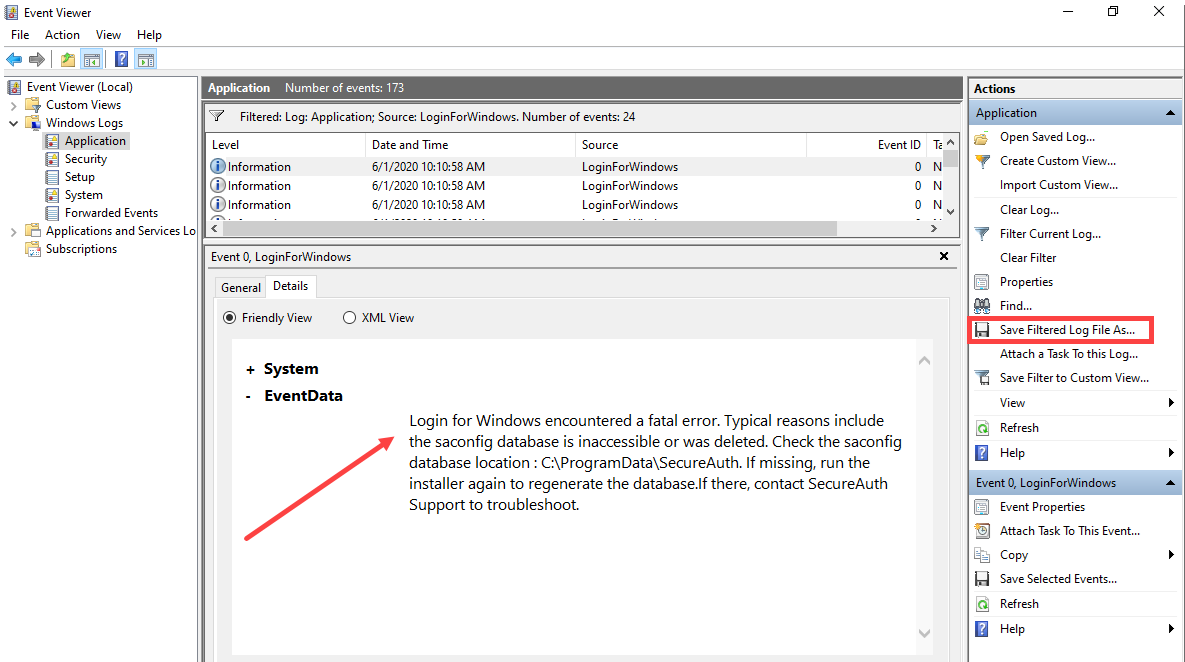
An end user receives a message that Login for Windows encountered an error, and guides them to try a different login method. As an administrator, you can check the Event Viewer to troubleshoot.
The following steps describe how to open the Event Viewer to read the event logs.
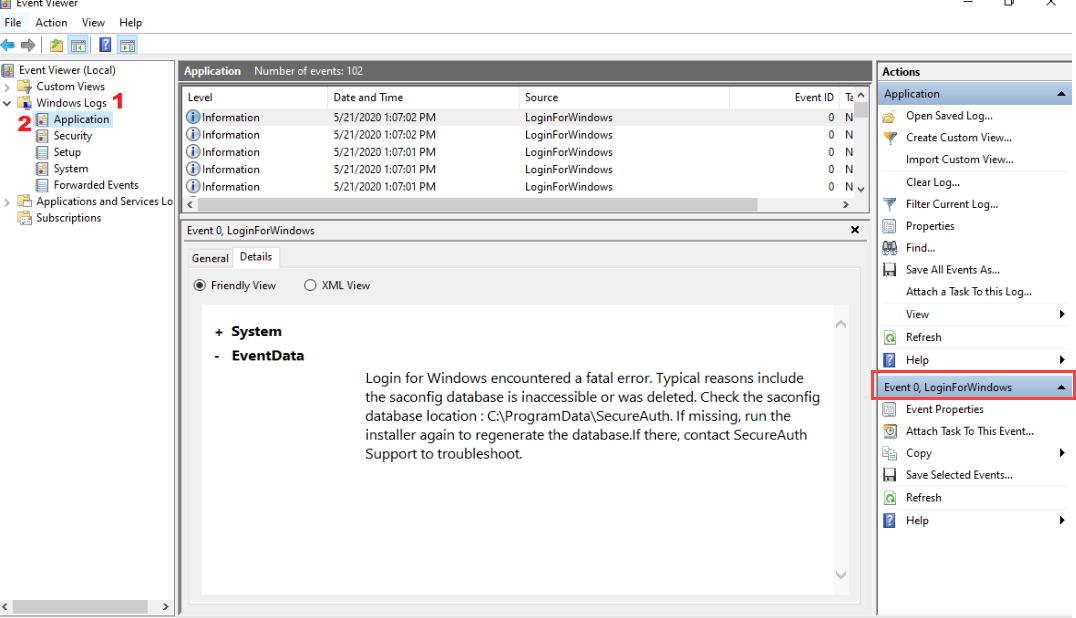
To view logs in Event Viewer
In the Windows Search bar, type
eventvwr.msc.Expand the Windows Logs folder and click Application, then Filter Current Log.
On the Filter Current Log window, in the Event sources field, type
LoginForWindows.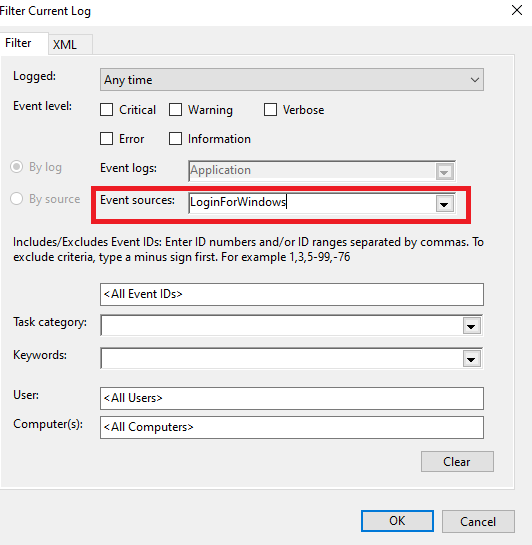
View the event information to troubleshoot the issue, as shown in the following example.
To export information, for example, to send to SecureAuth Support, click Save Filtered Log File As.