Adaptive Authentication Tab Configuration
Introduction
SecureAuth IdP's Adaptive Authentication starts immediately after a username is authorized against the enterprise directory, with an instant response to an authentication request. The Adaptive Engine's analysis determines whether a user should be passed, required to provide additional authentication, or denied access to the protected resource.
Adaptive Authentication thwarts breaches based on configured pre-authentication policies that require the bad actor to trigger one or more specified rules. For example, if the user attempts to authenticate from a blocked country (geo-location blocking), or attempts to VPN from a command-and-control server associated with a "bad" IP address (Threat Service), then authentication requirements are stepped-up, halting the bad actor's efforts.
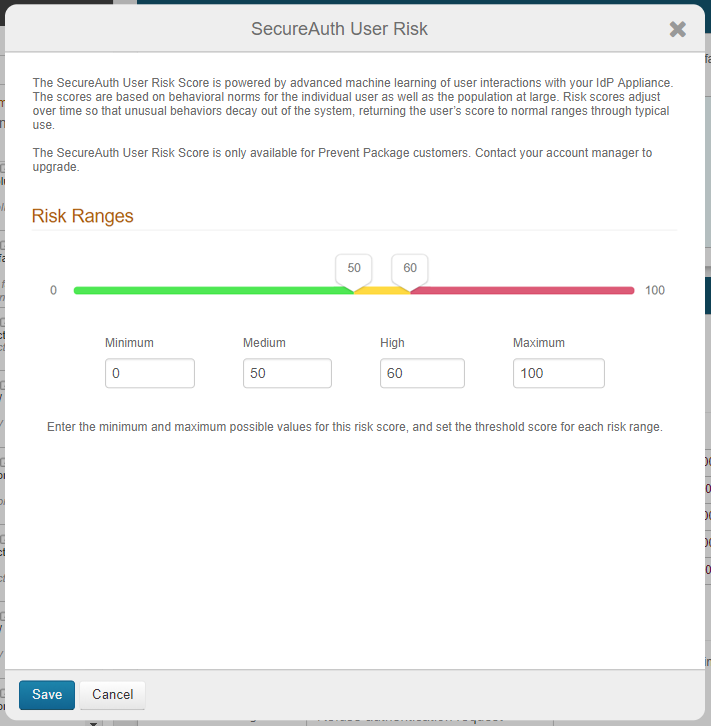
In SecureAuth IdP version 9.2, a new offering is available from SecureAuth's Prevent Threat Service package. Advanced adaptive capability powered by machine learning tracks and analyzes the login behavior patterns of authorized users for a period of time to identify their normal patterns, and then assigns each user a personal risk score. Bad actors' attempts to impersonate authorized users in order to gain access to the targeted site fail, since a login behavior pattern and risk score are unique to each user. See Machine learning User Risk Score calculations in Adaptive Authentication (version 9.2) and SecureAuth IdP 9.2.0-19 hotfix for machine learning deployment for more information.
Adaptive Authentication Features
Adaptive Authentication includes these features for enablement:
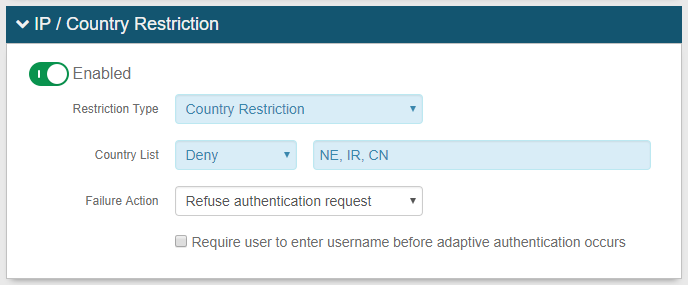
IP Address / Country Restriction: Restrict access by IP address(es) or country code(s)
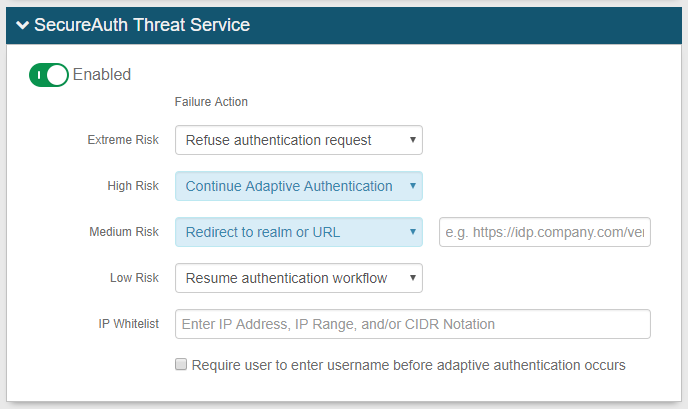
IP Reputation and Threat Detection (for version 9.1) or SecureAuth Threat Service (for version 9.2): Restrict access based on risk factors and threat intelligence by IP Address evaluation
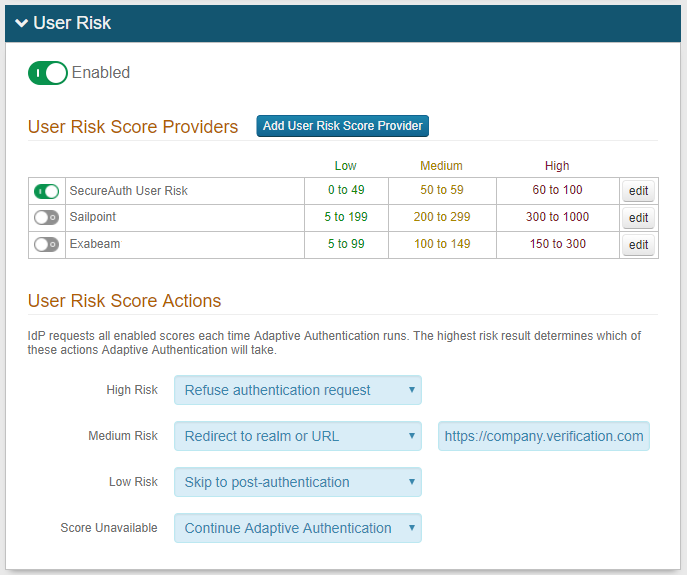
User Risk: Restrict access based on user reputation and / or user behavior factors
Any of the above features requires a special SecureAuth license – contact SecureAuth Support to upgrade
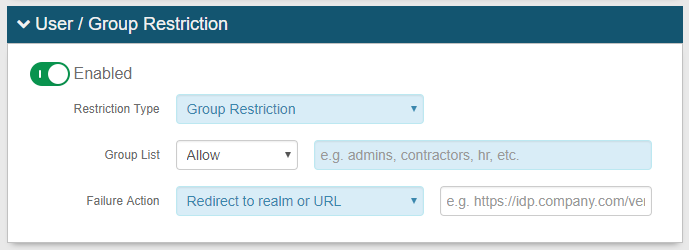
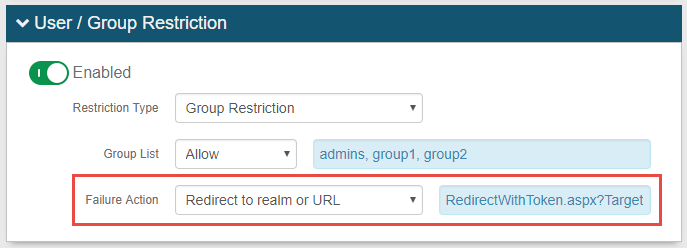
User / Group Restriction: Restrict access by end-user(s) or user group(s)
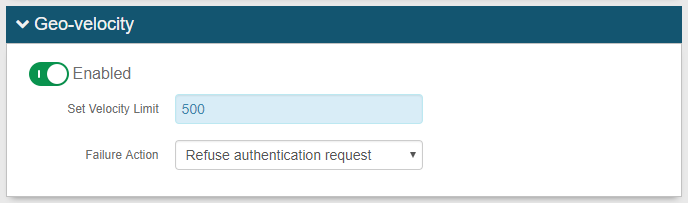
Geo-velocity Restriction: Restrict access based on the current time and location of end-user compared to time and location of end-user's last access
Adaptive Engine Actions
Prerequisites
1. Ensure SecureAuth IdP v9.1+ is running
2. Create a New Realm or access an existing realm in which Adaptive Authentication will be utilized in the SecureAuth IdP Web Admin
3. Configure the following tabs in the Web Admin in addition to configuring Adaptive Authentication:
Overview: the description of the realm and SMTP connections must be defined
Data: an enterprise directory must be integrated with SecureAuth IdP
Workflow: the way in which users will access the target must be defined
Multi-Factor Methods: the Multi-Factor Authentication methods that will be used to access the target (if any) must be defined
Post Authentication: the target resource or post authentication action must be defined
Logs: the logs that will be enabled or disabled for this realm must be defined
4. (OPTIONAL) Have a special SecureAuth IdP license to use IP Reputation / Threat Data analysis function (version 9.1) or SecureAuth Threat Service (version 9.2)
Contact SecureAuth Support to upgrade the SecureAuth IdP license
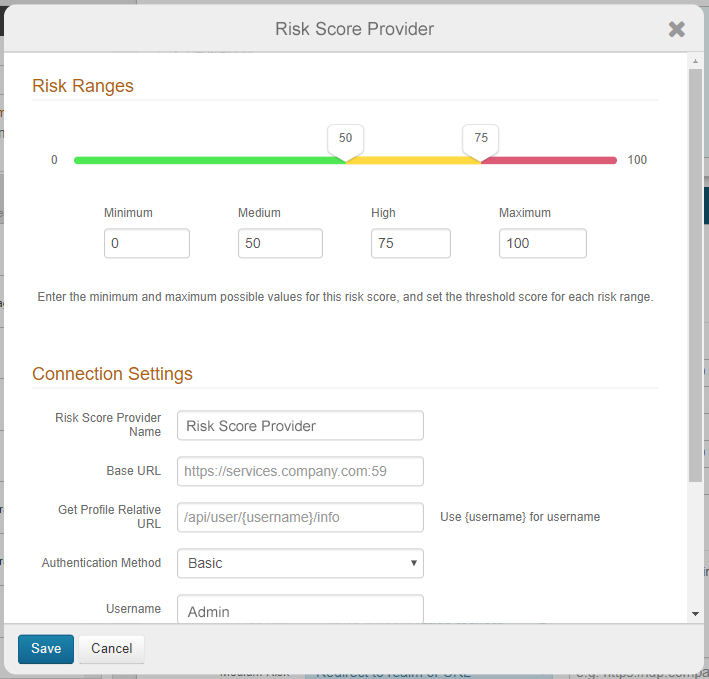
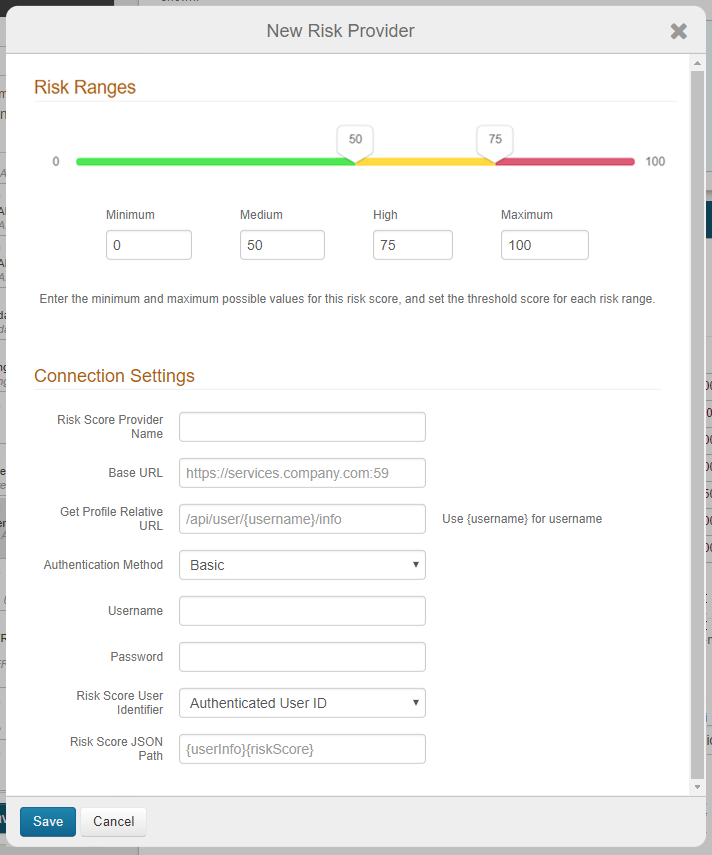
5. (OPTIONAL) Have an on-premises SailPoint IdentityIQ and / or Exabeam UEBA solution to use the User Risk analysis function
See Connecting SailPoint IdentityIQ to SecureAuth IdP 9.2 and / or Connecting Exabeam UEBA to SecureAuth IdP 9.2 for information about using SailPoint / Exabeam with SecureAuth IdP for the user risk score function
NOTE: In version 9.2,user risk analysis involves the use of risk scores to handle authentication requests. In version 9.1, policies are used to handle authentication requests.
Note
See Authentication API guide and Adaptive Authentication API Guide for information about configuring APIs
SecureAuth IdP Configuration Steps
Data
Note
This step is for LDAP data stores only, and if enabling the User / Group Restriction and / or Geo-velocity analysis features
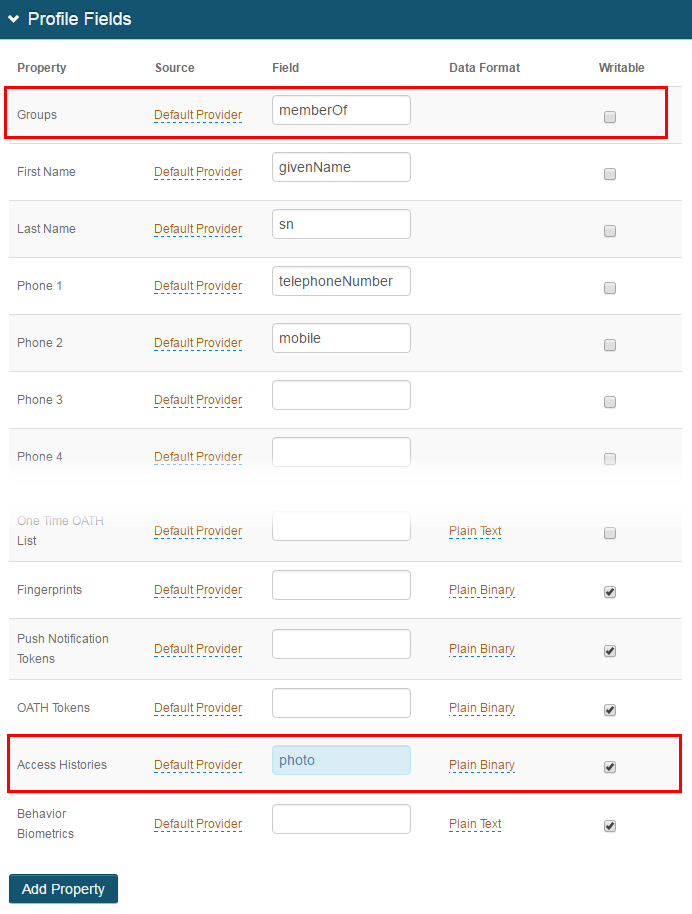 |
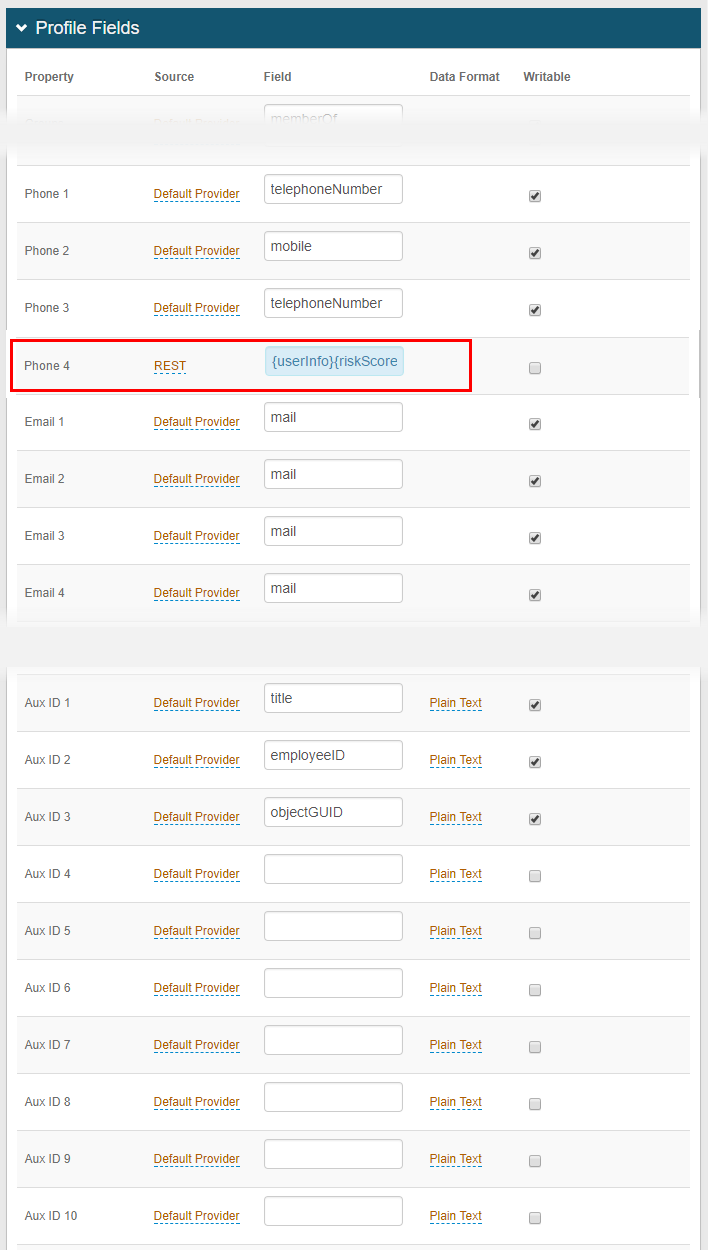
1. In the Profile Properties section, map the Groups property to the directory field (e.g. memberOf) that contains the user's group information in Active Directory
This step is required if enabling User / Group Restriction
2. Map the Access Histories Property to a directory field that fulfills the following requirements:
The Access Histories Property can be stored as Plain Binary or in JSON format, and has distinct requirements for the LDAP directory attribute mapped to the Property based on the Data Format selection
For Plain Binary, these requirements must be met for the directory field that contains the Access Histories information:
Length: 1024 minimum per Access History record (NOTE: The Access History setting is configured in the web.config file:<add key="AccessHistoryMaxCount" value="5" />)
Data Type: Octet string (bytes)
Multi-valued
For JSON, these requirements must be met for the directory field that contains the Access Histories information:
Length: No limit / undefined
Data Type: DirectoryString
Multi-valued
In typical AD deployments, the Data Format is Plain Binary and the photo directory field is utilized
3. Check Writable to allow SecureAuth IdP to write information to the Access Histories Property
Steps 2 - 3 are required if enabling Geo-velocity
Notice
The Properties must be mapped in each realm in which the User / Group Restriction and / or Geo-velocity analysis features are used
Warning
Click Save once the configuration has been completed and before leaving the Data page to avoid losing changes
Adaptive Authentication
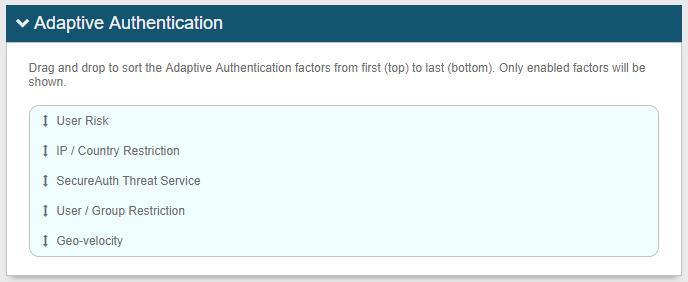 |
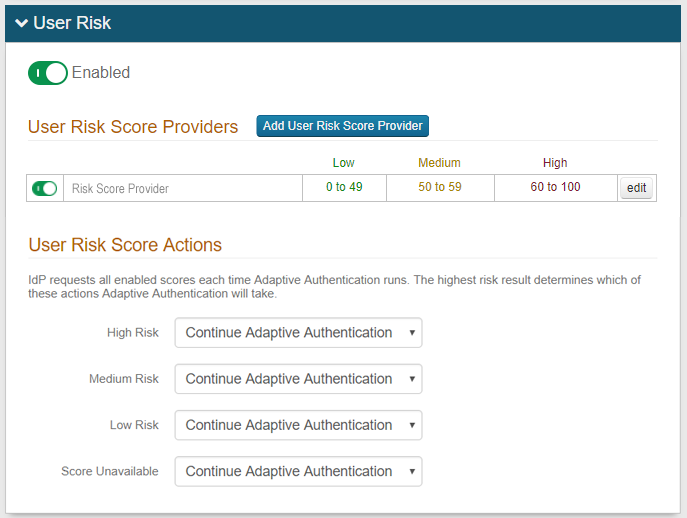
On the Adaptive Authentication page, in the Adaptive Authentication section, adaptive authentication factors enabled on this page appear in the table
Drag and drop selections to reorder the processing sequence
User Risk
Logging Features
Key-Value Pair Properties
Several key-value pair properties are placed in the structured data element of a syslog entry. These properties may also be logged in the header or message elements but are difficult to parse or extract.
Notice
NOTE: Not all properties introduced in these tables may appear in logs, since log data is set to show based on the SecureAuth Threat Service subscription level.
Threat Descriptions
Threat Types
The following values appear only in the realm's logs, and help to further classify the type of threat that is detected
Threat Categories
The following values appear only in the realm's logs, and help to further classify the type of threat that is detected